What is the difference between PD and PPS?
What is the difference between PD and PPS?
Fast charging is no longer just about speed; it is about efficiency, safety, and compatibility across multiple devices. USB Power Delivery has become the industry standard for modern charging, powering everything from smartphones to high-performance laptops through a single USB-C connection. Understanding the differences between Power Delivery 3.0, Power Delivery 3.1, and Programmable Power Supply (PPS) helps make sense of how today’s chargers deliver more power, adapt to device needs, and remain future-ready.

Understanding USB Power Delivery 3.0, 3.1 and PPS
As devices become more powerful, charging standards have evolved to meet demand. USB Power Delivery (PD) allows devices and chargers to negotiate power levels over USB, delivering faster, safer, and more efficient charging. The latest specifications—PD 3.0, PD 3.1, and Programmable Power Supply (PPS)—offer flexibility, higher power, and smarter battery management.
PD 3.0: Flexible Power and Efficiency
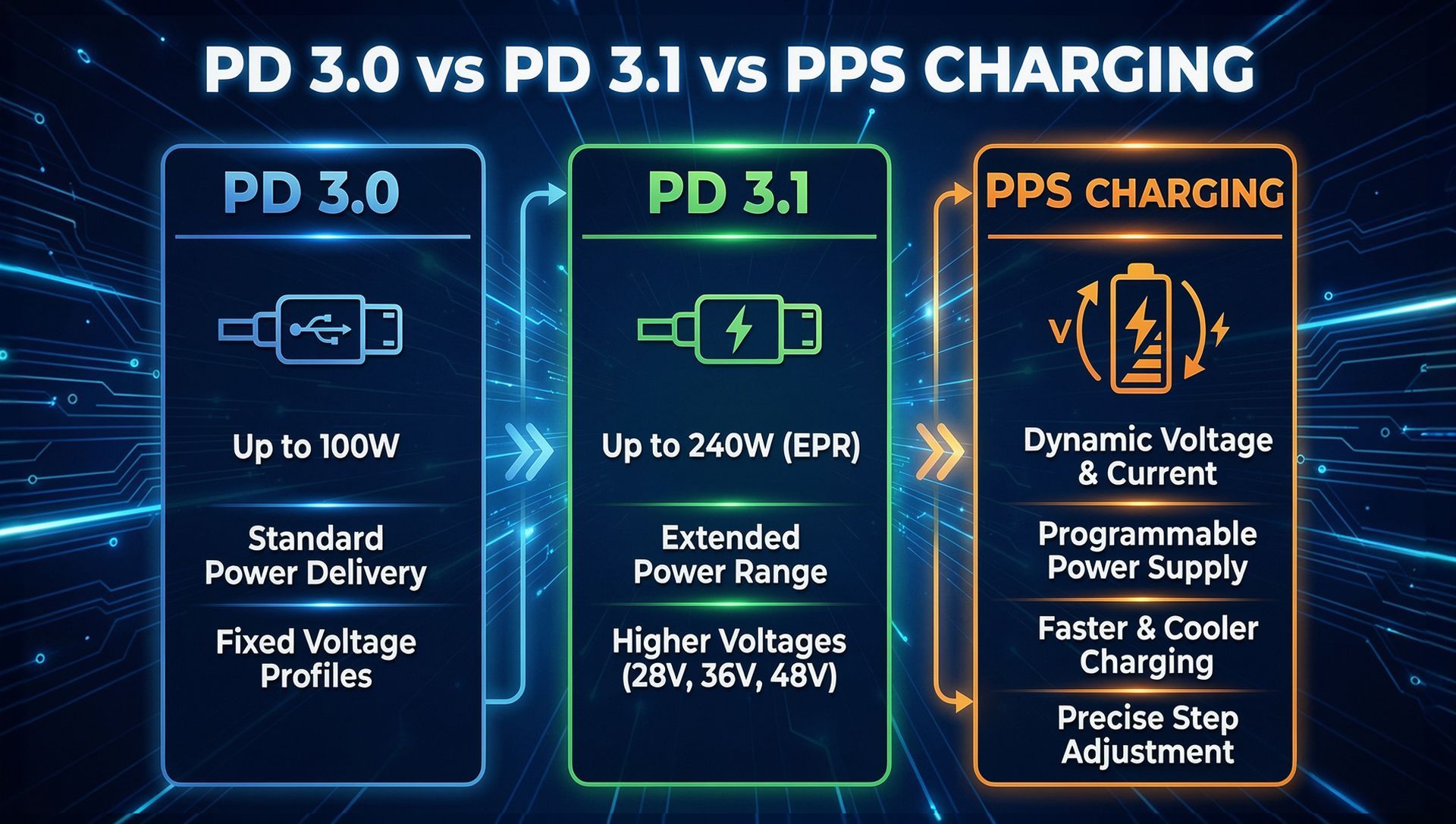
PD 3.0 built on earlier versions with extended power profiles, improved efficiency, and better device–charger communication. It allowed devices to choose the most suitable voltage, typically 5 V, 9 V, 15 V, or 20 V, based on their battery state. This flexibility reduced energy loss, improved heat management, and protected battery health. PD 3.0 also introduced security features to ensure chargers and devices communicated safely. Widely adopted across phones, tablets, laptops, and accessories, PD 3.0 remains a standard for fast and reliable charging.
PD 3.1: Higher Power for Modern Devices
PD 3.1 addresses the increasing power needs of larger devices. Its standout feature is the Extended Power Range (EPR), which allows up to 48 V at 5 A, delivering up to 240 W—enough for high-performance laptops, monitors, and even some desktop systems. PD 3.1 introduces new voltage levels such as 28 V, 36 V, and 48 V, but high-power operation requires EPR-rated cables for safety. PD 3.1 is backward compatible with PD 3.0, ensuring older devices still operate at traditional power levels.
PPS: Dynamic and Adaptive Charging
While PD provides flexible fixed voltages, PPS allows devices to adjust voltage and current dynamically during charging. Devices can request precise voltage steps, for example from 3.3 V to 11 V in 20 mV increments, optimising efficiency and reducing heat. PPS is particularly useful for smartphones and tablets, improving battery longevity and comfort by keeping devices cooler during fast charging. It works alongside PD 3.x, adding adaptive control without breaking compatibility.
Comparing the Standards
- PD 3.0: Flexible fixed voltages up to 100 W, broad ecosystem support.
- PD 3.1: Higher power up to 240 W, new voltages, requires EPR-rated cables, ideal for laptops and larger devices.
- PPS: Dynamic voltage and current control, better efficiency and thermal management, especially for battery-centric devices.
| Feature | PD 3.0 | PD 3.1 | PPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Power | Up to 100 W | Up to 240 W | Depends on PD version |
| Maximum Voltage | 20 V | 48 V (EPR) | Variable, typically 3.3 V to 21 V |
| Current | Up to 5 A | Up to 5 A | Dynamically adjusted |
| Voltage Type | Fixed voltage steps | Fixed voltage steps including higher voltages | Continuously adjustable in small steps |
| Key Advantage | Reliable fast charging across many devices | Supports high-power laptops and larger devices | Optimised efficiency and reduced heat |
| Cable Requirements | Standard USB-C PD cable | EPR-rated USB-C cable for high power | Standard PD cable (device dependent) |
| Backward Compatible | Yes | Yes, falls back to PD 3.0 | Yes, works within PD 3.x |
| Best For | Phones, tablets, laptops up to 100 W | High-performance laptops, monitors, workstations | Smartphones and battery-focused devices |
| Thermal Performance | Good | Good | Excellent |
| Battery Health Impact | Improved vs legacy charging | Improved vs legacy charging | Best-in-class battery protection |
Why it Matters
Understanding these standards is crucial for designers, engineers, and resellers. PD 3.x and PPS allow one charger to serve multiple devices, improve battery health, and maintain interoperability across ecosystems. PD 3.1 future-proofs USB-C, enabling it to replace proprietary high-power connectors on larger devices. Selecting the right charger involves checking power ratings, PPS support, and using appropriate cables for safety.
Conclusion
USB Power Delivery has redefined charging. PD 3.0 offers flexible profiles and efficiency; PD 3.1 brings high-power capabilities up to 240 W; and PPS enables intelligent, adaptive charging. Together, they ensure faster, safer, and more reliable charging across a wide range of devices, making USB-C a truly universal standard. As SKROSS continues to expand its range with PD 3.1 and EPR-enabled products, travellers and tech enthusiasts alike can expect a universal, safe, and high-performance charging experience wherever their devices take them.
Check our the SKROSS power delivery range here